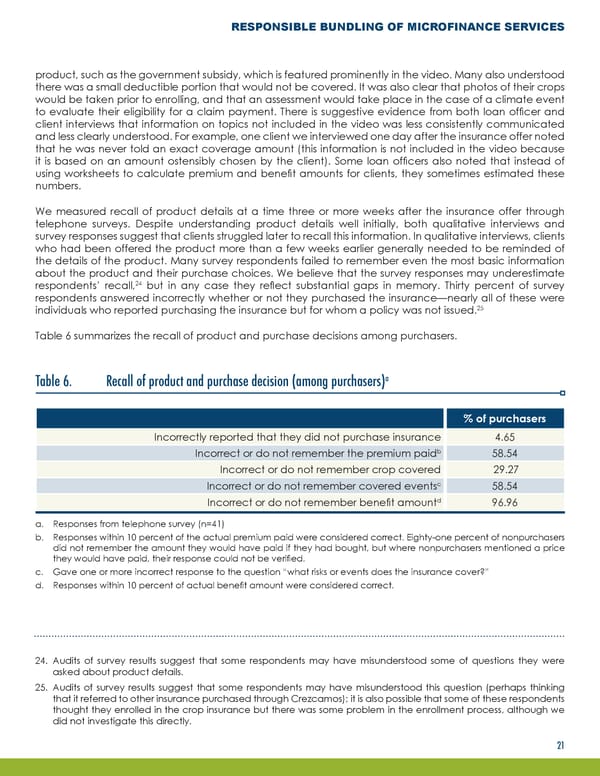
RESPONSIBLE BUNDLING OF MICROFINANCE SERVICES product, such as the government subsidy, which is featured prominently in the video. Many also understood there was a small deductible portion that would not be covered. It was also clear that photos of their crops would be taken prior to enrolling, and that an assessment would take place in the case of a climate event to evaluate their eligibility for a claim payment. There is suggestive evidence from both loan officer and client interviews that information on topics not included in the video was less consistently communicated and less clearly understood. For example, one client we interviewed one day after the insurance offer noted that he was never told an exact coverage amount (this information is not included in the video because it is based on an amount ostensibly chosen by the client). Some loan officers also noted that instead of using worksheets to calculate premium and benefit amounts for clients, they sometimes estimated these numbers. We measured recall of product details at a time three or more weeks after the insurance offer through telephone surveys. Despite understanding product details well initially, both qualitative interviews and survey responses suggest that clients struggled later to recall this information. In qualitative interviews, clients who had been offered the product more than a few weeks earlier generally needed to be reminded of the details of the product. Many survey respondents failed to remember even the most basic information about the product and their purchase choices. We believe that the survey responses may underestimate 24 respondents’ recall, but in any case they reflect substantial gaps in memory. Thirty percent of survey respondents answered incorrectly whether or not they purchased the insurance—nearly all of these were 25 individuals who reported purchasing the insurance but for whom a policy was not issued. Table 6 summarizes the recall of product and purchase decisions among purchasers. Table 6. Recall of product and purchase decision (among purchasers)a % of purchasers Incorrectly reported that they did not purchase insurance 4.65 b Incorrect or do not remember the premium paid 58.54 Incorrect or do not remember crop covered 29.27 c 58.54 Incorrect or do not remember covered events d 96.96 Incorrect or do not remember benefit amount a. Responses from telephone survey (n=41) b. Responses within 10 percent of the actual premium paid were considered correct. Eighty-one percent of nonpurchasers did not remember the amount they would have paid if they had bought, but where nonpurchasers mentioned a price they would have paid, their response could not be verified. c. Gave one or more incorrect response to the question “what risks or events does the insurance cover?” d. Responses within 10 percent of actual benefit amount were considered correct. 24. Audits of survey results suggest that some respondents may have misunderstood some of questions they were asked about product details. 25. Audits of survey results suggest that some respondents may have misunderstood this question (perhaps thinking that it referred to other insurance purchased through Crezcamos); it is also possible that some of these respondents thought they enrolled in the crop insurance but there was some problem in the enrollment process, although we did not investigate this directly. 21
 Responsible Bundling of Microfinance Services Page 23 Page 25
Responsible Bundling of Microfinance Services Page 23 Page 25